Superposition Principle - Understanding the Most Fundamental Principle in Physics
The Superposition Principle: Exploring the Fundamental Concept in Physics
Physics, as a discipline, is built on a foundation of fundamental principles that help us understand the intricacies of the universe. One such principle is the superposition principle.
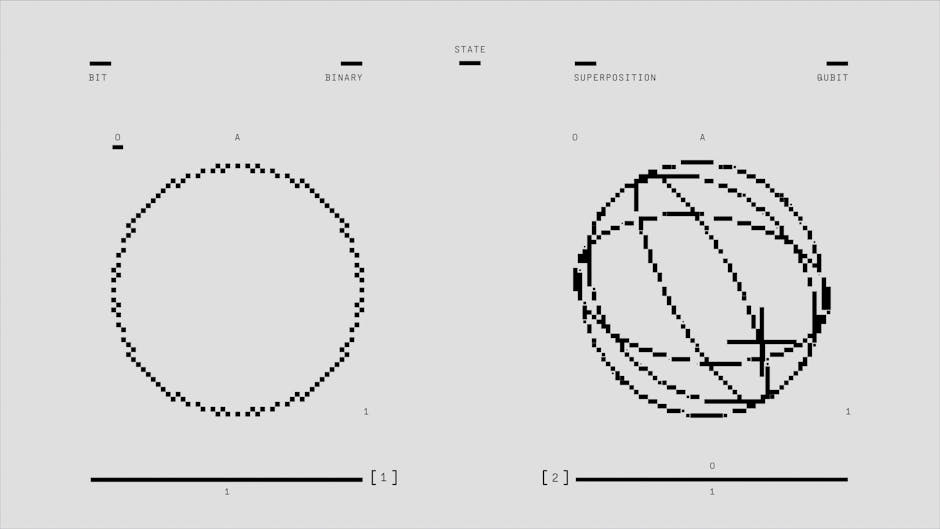
The superposition principle states that when two or more physical states are combined, the resulting state is determined by the algebraic sum of the individual states. In simpler terms, the principle explains how multiple states can exist simultaneously and can add up to create new states.
This concept is particularly relevant in the field of quantum mechanics, where particles are described by wave functions and can exist in multiple states at once. Superposition allows us to understand how particles can exhibit wave-like properties and have multiple probabilities of different states.
One of the classic examples to understand the superposition principle is the famous double-slit experiment. In this experiment, a beam of particles, such as electrons or photons, passes through two slits and creates an interference pattern on the screen behind. The interference pattern is the result of the superposition of the possible paths the particles can take.
The applications of the superposition principle stretch across various scientific fields. In quantum computing, superposition is used to perform multiple calculations simultaneously, leveraging the immense computational power it offers. In quantum cryptography, superposition ensures secure communication by encoding messages in quantum states, making it nearly impossible to intercept or decode.
Understanding the superposition principle provides a solid foundation for comprehending more complex concepts in physics. It challenges our intuitions about how the physical world works and opens up doors to innovative technologies and advancements.
To summarize, the superposition principle is an essential concept that explains how multiple physical states can combine to create new states. Its applications in fields like quantum mechanics, computing, and cryptography are revolutionary and have paved the way for groundbreaking discoveries and technologies.
